24. November 2025 By Julian Biedermann and Fabian Rump
Android XR: App design and development in a new dimension
The market for extended reality (XR), the umbrella term for all technologies that merge the real and digital worlds, is more mature than ever. It promises to fundamentally change the way we interact, work and play. For a long time, the race for supremacy seemed clearly divided. Apple is focusing on the high-end segment with Vision Pro and the visionOS operating system, while Meta is targeting the mass market with the Quest series and Ray-Ban Smart Glasses with Horizon OS.
But now Google, another tech giant from Silicon Valley, is entering the fray and bringing a breath of fresh air to the world of extended reality with Android XR. The company is taking a completely new approach: instead of relying on a closed system, Google is opening the doors to innovation. Android XR is an open operating system that gives manufacturers worldwide the freedom to develop a new generation of devices – from impressive VR headsets and state-of-the-art AR glasses to stylish smart glasses suitable for everyday use. The result is a versatile ecosystem that redefines the future of virtual and augmented reality.
The big advantage here is the deep integration of Gemini, Google's in-house AI, which is designed to bring contextual intelligence into everyday life. Android XR also benefits from the huge existing Android ecosystem, which means that millions of existing 2D apps can potentially run immediately on compatible devices – an immense advantage when entering the market.
The first Android XR-based device is already in the starting blocks: Samsung's Galaxy XR mixed reality headset. It is positioned as a direct competitor to Apple and Meta's offerings and marks the beginning of a new phase in the competition for the XR market. This development shows that the race for the future of virtual and augmented reality is only just beginning and that Google wants to play a central role in it with Android XR.

The new Galaxy XR headset with Android XR as its operating system, source: https://news.samsung.com/de/samsung-galaxy-xr-der-start-in-neue-digitale-welten
App modes and design guidelines
A key feature of the Android XR experience is the two basic modes in which applications can be run.
In the so-called ‘Home Space’, the device becomes an efficient multitasking centre: apps appear as floating, flexible 2D windows that can be freely arranged in space and used in parallel with other applications. This mode is automatically supported by all compatible Android apps – a huge advantage, as it means that millions of existing applications can run immediately on XR devices.
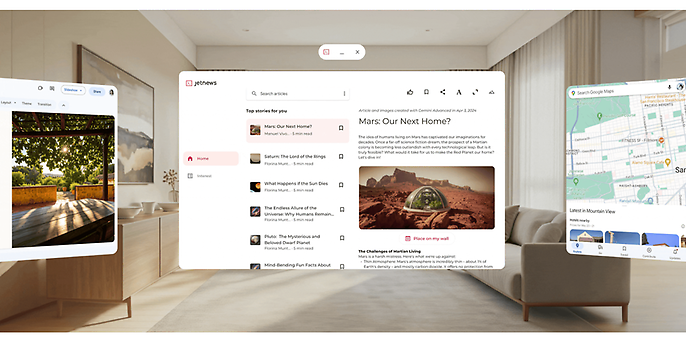
Several different Android apps side by side in the room in what is known as ‘Home Space’ mode, source: https://developer.android.com/xr?hl=de
For an enhanced, immersive experience, developers can gradually add spatial interactions to their apps. When users want to fully immerse themselves in an application – such as a 3D game, a film on a virtual big screen or an interactive room display – they can switch to ‘Full Space’ mode. Here, the app takes over the entire visible space, blocks out distractions and can use all 3D and XR functions of Android XR, provided they are implemented in the app. The aim is to either seamlessly embed digital content into the physical environment or to move around in a virtual environment – intuitively controllable via natural inputs such as hand gestures, gaze direction or speech.
XR requires a radically new understanding of design. Instead of two-dimensional surfaces, the focus is on spatial arrangement, perspective, movement behaviour and ease of use. In its guidelines, Google emphasises the following principles in particular:
1. Use spatial freedom
In the world of XR, the boundaries of the classic screen disappear. Content is no longer displayed on a surface, but is freely placed in the space around the user. This creates new opportunities for interaction, storytelling and presentation – more intense, natural and immersive than ever before.
2. Focus on key moments
Good XR experiences do not consist of constant events, but of targeted highlights. Situations should be identified in which the app can impress – for example, through surprising interactions, memorable animations or strong visual elements.
3. Comfort over complexity
XR must not be overwhelming. Large fonts, comfortable viewing angles and reduced movement ensure that users feel comfortable even during prolonged use.
4. Adapt familiar patterns
Familiar navigation elements such as buttons, menus or gestures can be adopted in XR and meaningfully expanded with spatial interactions.
App development and mobile solutions
Mobile Business @ adesso
From concept and design to development and support: we accompany your mobile transformation – cross-platform, efficient and tailor-made. Develop mobile solutions with us that optimise processes, empower employees and secure your future.
Jetpack XR SDK and Android Studio Support
The Jetpack XR SDK is available to developers for the technical implementation of the modes and principles presented above. It enables the free placement of familiar UI components in space using so-called ‘spatial layouts’ without having to completely overhaul the existing app architecture. The XR emulator integrated into Android Studio also allows realistic previewing and optimisation of these enhancements directly on the desktop.
This close connection to the existing Android ecosystem significantly lowers the barrier to entry and creates the basis for adding immersive content to classic ‘2D apps’ at any time.
Jetpack XR is at the heart of technical XR development on Android. The most important components of the SDK are:
- Compose XR: Spatial UI components such as panels, orbits and floating layouts can be freely positioned in space.
- SceneCore: A 3D graphics engine for models, environments and animations.
- Material Design for XR: Adapted to the requirements of spatial representations.
- ARCore integration: For motion tracking, plane detection and so-called ‘anchor placement’.
The Android Studio version that first offered stable support for Android XR was ‘Android Studio Narwhal | 2025.1.4 Feature Drop’. However, the current preview releases (Canary Builds) offer the widest range of XR features and the best compatibility with the latest versions of the XR libraries. These are currently still in alpha status. The feature set of Android XR in Android Studio includes an XR emulator, the layout inspector with XR support, and an XR project template with the necessary Jetpack XR SDK libraries. However, Canary versions are in early stages of development and may be unstable. Therefore, they should be used with caution.
Showcase app ‘Fish Viewer’
To get to know the new operating system, the Android XR SDK and the new design guidelines better, we have created a small showcase app called ‘Fish Viewer’ as part of this blog post and published it on a repository on GitHub.
The application allows you to view different species of fish and learn interesting facts about them. It is structured as a list of fish names, each of which has a detail page containing information such as a picture and a description of the selected fish.
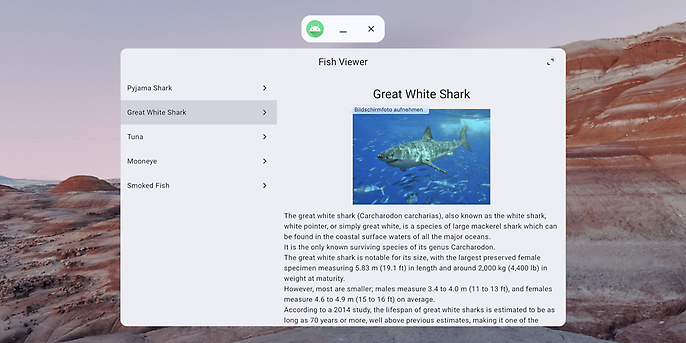
The Fish Viewer app in Home Space mode
Above the main content is an app bar that contains the centred app title and an icon button with two arrows on the right-hand side, which is only visible when the application is running on a device that supports XR content. This can be queried in the code using the `hasXrSpatialFeature` field of the Composition Local `LocalSpatialConfiguration`. If this button is interacted with in Home Space mode, the app switches to Full Space mode. This can be achieved with the `requestFullSpaceMode` function of the same Composition Local. To determine programmatically which mode the app is in so that immersive components can be shown or hidden accordingly, another Composition Local can be used: `LocalSpatialCapabilities` with the field `isSpatialUiEnabled`.
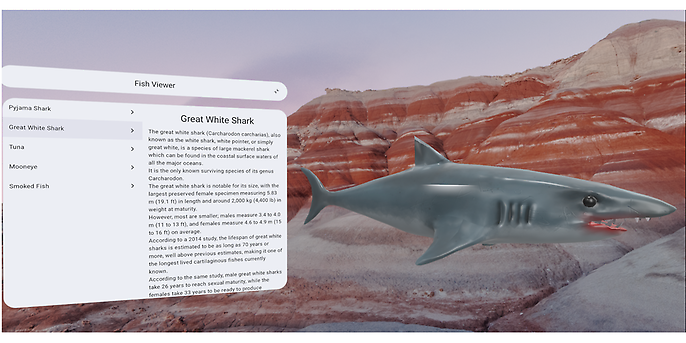
The Fish Viewer app in full space mode
Once in Full Space mode, two changes immediately catch the eye, which should not overwhelm users (design guideline 3).
The app bar is no longer directly linked to the main content, but now ‘floats’ slightly above it. This behaviour could be achieved with a new XR UI component called Orbiter. However, in this case, the app bar automatically supports this behaviour when it is in Full Space mode and this has been explicitly activated in the code. To do this, it only needs to be located within the new composable `EnableXrComponentOverrides`. To activate all supported UI components in an app, the corresponding composable can be placed at the top level of the app. However, please note that the `ListDetailPaneScaffold` used in the showcase app, which also supports an immersive form, does not currently work in this state due to a library version conflict.
The two widely used components `CenterAlignedTopAppBar` and `ListDetailPaneScaffold` were chosen here in order to adapt familiar patterns from existing apps so that users can immediately find their way around (Design Guideline 4).
The new freedom in full space mode is also put to good use by displaying a 3D model of the fish on the right-hand side of the detail page next to the main content instead of an image (design guideline 1). This gives users a much better impression of the selected fish compared to a two-dimensional image and allows them to move it around and place it anywhere in the room. This immersive experience is definitely a highlight of the app and can leave a positive impression (Design Guideline 2).
Technically, the application in Full Space mode is structured as a `SpatialRow`, which consists of a `SpatialPanel` (left) and a `SpatialBox` with a `Volume`. The `SpatialPanel` can be resized and moved around the room. The 3D models of the fish are loaded into the `Volume` as GLB files, given a specific pose and scale, and can also be moved. The Compositon Local `LocalSession` is required to load the models, and in general, all immersive components must always be located within the `Subspace` component in order to function.
The app was implemented using the following libraries from the Android XR SDK, whose versions were current at the time of publication of the blog post:
- Runtime XR: 1.0.0-alpha06
- Compose XR: 1.0.0-alpha07
- Material 3 XR: 1.0.0-alpha11
- SceneCore: 1.0.0-alpha07
A promising future
Android XR opens up new perspectives for the design and development of immersive applications. With its open approach, it differs significantly from Apple's visionOS and Meta's Horizon OS: thanks to the support of numerous manufacturers and integration into the existing Android ecosystem, developers can serve a wide range of devices and potentially make existing apps usable immediately. Close integration with Gemini, Google's AI platform, also offers the possibility of incorporating contextual intelligence directly into XR applications.
In practice, the Jetpack XR SDK, the Android XR Emulator and the ARCore platform provide powerful tools that facilitate the development of spatial user interfaces and 3D experiences. XR requires a new understanding of design: content is positioned in space, interactions must be comfortable and intuitive, and familiar UI patterns can be meaningfully transferred to spatial representation.
With Samsung's Galaxy XR as the first Android XR device, the implementation of these technologies is becoming tangible and the market for XR devices is becoming more dynamic. Overall, Android XR offers developers the opportunity to create innovative, immersive experiences and position themselves early on in a growing market.
adesso has already gained a wealth of experience in the field of XR and has implemented several projects in this area. Accordingly, our experts in the field of mobile applications have extensive expertise, including apps on XR devices. Successful projects include the development of a mixed reality test environment for UX and cockpit concepts in collaboration with the BMW Group and the implementation of a virtual reality training centre for occupational safety called ‘Safety Street VR’ for RWE Generation SE.
We support you!
adesso accompanies you every step of the way into the world of Android XR – from strategic consulting and the design of spatial experiences to technical implementation. Together, we develop immersive applications that expand your digital future.


